Friday, May 29, 2009
AIX snapshot cpmmand
Purpose
Modify, create or view properties of enhanced journaled file system (JFS2) snapshots.
Syntax
To Create an External Snapshot
snapshot -o snapfrom=snappedFS snapshotLV
snapshot -o snapfrom=snappedFS -o size=Size
To Create an Internal Snapshot
snapshot -o snapfrom=snappedFS -n snapshotName
Full Information
Wednesday, May 27, 2009
rule Blank Sender on IMSS
 information
informationTuesday, May 26, 2009
7 Troubleshoot Commands for young admin
1. IPconfig
/all -This option will display for all network information of this computer --> Computer name, Joined domain or work group, IP address, Gateway, DNS, WIN, DHCP IP & etc.
/renew -Renew the IP address for the specified adapter.
/flushdns -Purges the DNS Resolver cache.
/displaydns -Display the contents of the DNS Resolver Cache. http://technet2.microsoft.com/windowsserver/en/library/7356d145-e8ee-4dae-9edb-8b08a37e53841033.mspx?mfr=true
2.Route sub command of NetSH
route PRINT
route ADD
157.0.0.0 MASK 255.0.0.0 157.55.80.1 METRIC 3 IF 2
Destination ^mask {Gateway IP} ^gateway metric ^ Interface ^IF number
3.Ping
Test acknowledge from destination
-t Ping the specified host until stopped. To see statistics and continue - type Control-Break; To stop - type Control-C.
-a Resolve addresses to hostnames. -n count Number of echo requests to send.
-l size Send buffer size.
-f Set Don't Fragment flag in packet (IPv4-only).
-i TTL Time To Live.
-v TOS Type Of Service (IPv4-only).
-r count Record route for count hops (IPv4-only).
-s count Timestamp for count hops (IPv4-only).
-j host-list Loose source route along host-list (IPv4-only).
-k host-list Strict source route along host-list (IPv4-only).
-w timeout Timeout in milliseconds to wait for each reply.
-R Trace round-trip path (IPv6-only).
4.Tracert
See route of network packet from source to destination
• -d Do not resolve addresses to hostnames.
• -h maximum_hops Maximum number of hops to search for target.
• -j host-list Loose source route along host-list (IPv4-only).
• -w timeout Wait timeout milliseconds for each reply.
• -R Trace round-trip path (IPv6-only).
• -S srcaddr Source address to use (IPv6-only).
• -4 Force using IPv4.
• -6 Force using IPv6.
5.Arp
See detail of mapping IP table with MAC address
-a Displays current ARP entries by interrogating the current protocol data. If inet_addr is specified, the IP and Physical addresses for only the specified computer are displayed. If more than one network interface uses ARP, entries for each ARP table are displayed.
-s Adds the host and associates the Internet address inet_addr with the Physical address eth_addr. The Physical address is given as 6 hexadecimal bytes separated by hyphens. The entry is permanent.
-d Deletes the host specified by inet_addr. inet_addr may be wildcarded with * to delete all hosts.
Main problem of VIP (NLB or cluster)
6.Telnet
Test destination TCP service port over network & FW
telnet {destination IP} {service port}
7.Netstat
• -a Displays all connections and listening ports.
• -b Displays the executable involved in creating each connection or listening port.
In some cases well-known executables host multiple independent components, and in these cases the sequence of components involved in creating the connection or listening port is displayed. In this case the executable name is in [] at the bottom, on top is the component it called, and so forth until TCP/IP was reached. Note that this option can be time-consuming and will fail unless you have sufficient permissions.
• -e Displays Ethernet statistics. This may be combined with the -s option.
• -n Displays addresses and port numbers in numerical form.
• -o Displays the owning process ID associated with each connection.
• -p proto Shows connections for the protocol specified by proto;
proto may be any of: TCP, UDP, TCPv6, or UDPv6. If used with the –s option to display per-protocol statistics, proto may be any of: IP, IPv6, ICMP, ICMPv6, TCP, TCPv6, UDP, or UDPv6.
• -r Displays the routing table.
• -s Displays per-protocol statistics.
By default, statistics are shown for IP, IPv6, ICMP, ICMPv6, TCP, TCPv6, UDP, and UDPv6; the -p option may be used to specify a subset of the default.
• -t Displays the current connection offload state.
• -v When used in conjunction with -b, will display sequence of components involved in creating the connection or listening port for all executables.
• Interval Redisplays selected statistics, pausing interval seconds between each display. Press CTRL+C to stop redisplaying statistics. If omitted, netstat will print the current configuration information once.
Load Document
Office Scan Client/Server Edition 8
Manual
site reference www.trendmicro.com
Manually updating the Pattern File for the OfficeScan
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
On the OfficeScan Server:
1.Download the Official Pattern Release (OPR) or Controlled Pattern Release (CPR)
2.Extract the pattern file (lpt$vpn.xxx) to the PCCSRV folder.
Note: xxx = pattern file version
On the OfficeScan client:
1.Download the Official Pattern Release (OPR) or Controlled Pattern Release (CPR)
For Windows 95/98 client machines:
1.Right-click the OfficeScan icon in the Windows taskbar and select Unload OfficeScan Monitor from the pop-up menu.
2.Enter the unload password.
3.Extract the pattern file (lpt$vpn.xxx, where xxx is the pattern file number) to the OfficeScan Home directory. By default, this is \Program Files\OfficeScan Client.
4.Load the OfficeScan Monitor by selecting Start > Programs > Trend OfficeScan Win95 > OfficeScan95.
For Windows NT/2000/XP client machines:
1.Logon to the workstation as an administrator.
2.Go to Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Services.
3.Stop the following services:
• OfficeScanNT Listener
• OfficeScanNt RealTime Scan
4.Extract the pattern file (lpt$vpn.xxx, where xxx is the pattern file number) to the OfficeScan home directory. By default, this is OfficeScan Client.
5.Restart the following services:
• OfficeScanNT Listener
• OfficeScanNt RealTime Scan
Full Manual
site reference www.trendmicro.com
Monday, May 25, 2009
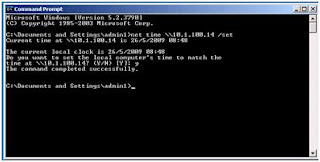
Set Net Time connect to NTP Server
net time /setsntp:<server name>
 and connect to private time server
and connect to private time servernet time \\server_ip_address /set
Friday, May 22, 2009
Enable Form Base Authentication
Thursday, May 21, 2009
OWA Log Off Button
 When I logoff from OWA, window popup windows authentication again. If I click on Cancel, I get an error message about "Access denied." At this point if I use I.E.'s Back button, it will go back to my mailbox again. It’s not secure. As show below.
When I logoff from OWA, window popup windows authentication again. If I click on Cancel, I get an error message about "Access denied." At this point if I use I.E.'s Back button, it will go back to my mailbox again. It’s not secure. As show below.Information Here
Managing permissions on connections
Managing Permissions on a per-connection basis
Terminal Services Configuration allows you to manage permissions on an individual connection by means of the Permissions tab in the connection Properties page.
The TCP/IP connection installed with Terminal Services comes with a set of default permissions. You can modify these default permissions by setting different permissions for different users or groups, adjusting them to fit the requirements of your organization. You must be logged on as a member of the Administrators group to manage connection permissions.
The default permissions on Terminal Services objects are as follows:
Group Permission
Administrators Full control
LOCAL SERVICE Service permissions
NETWORK SERVICE Service permissions
Remote Desktop Users User access
SYSTEM Full control
Guest Guest access
For information about managing permissions for users and groups, see Adding users and groups. For information about the types of permissions used to control access to Terminal Services, see Controlling connection access.
Wednesday, May 20, 2009
assign permission remote (RDP-Tcp)
After you add user to Remote Desktop Users Group but can’t remote

How To Add a user or group from permission lists
1. Open Terminal Services Configuration.
2. In the console tree, click Connections.
4. On the Permissions tab, in Group or user names:, select the user or group you want to add, and then click Add.

Notes
To perform this procedure, you must be a member of the Administrators group on the local computer, or you must have been delegated the appropriate authority. If the computer is joined to a domain, members of the Domain Admins group might be able to perform this procedure. As a security best practice, consider using Run as to perform this procedure.
To open Terminal Services Configuration, click Start, click Control Panel, double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Terminal Services Configuration.
You must use the Remote Desktop Users group to control remote access to Terminal Server and Remote Desktop for Administration.
Related Topics
Tuesday, May 19, 2009
How to clear local DNS cache
Fibre Channel over Ethernet
Jump to: navigation, search
Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) is a proposed mapping of Fibre Channel frames over full duplex IEEE 802.3 networks. This allows Fibre Channel to leverage 10 Gigabit Ethernet networks while preserving the Fibre Channel protocol. The specification is supported by a large number of network and storage vendors, including Dune Networks, Absolute Analysis, ATTO Technology, BLADE Network Technologies, Bloombase, Broadcom, Brocade, Cisco, EMC, Emulex, XOdyne, Finisar, HP, IBM, Intel, Hitachi Data Systems, Mellanox, NetApp, PMC-Sierra, QLogic and Sun Microsystems.
Contents[hide]
1 Functionality
2 Application
3 Frame Format
4 Timeline
5 See also
6 External links
Thank you for reference site: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FCoE
Change Domain Admin Password in W2K3 AD

Monday, May 18, 2009
Edit HD Wizard on Hyper–V
Saturday, May 16, 2009
HowToInstallOracleClient
 Run file://dogbert.mse.cs.cmu.edu/TabletPC/Tools/OracleClient/Disk1/SETUP.EXE
Run file://dogbert.mse.cs.cmu.edu/TabletPC/Tools/OracleClient/Disk1/SETUP.EXEThursday, May 14, 2009
Installing openSSH on AIX 5.1-3
Installing openSSH on AIX 5.1-3
At 5.1, 5.2, and 5.3, the installation of openssh itself is in installp format, but all the prerequisites (including openssl) can be installed using the same rpm -i commands (using the same 4.3.3. rpm packages). The installp format package can be downloaded from the following site:http://sourceforge.net/projects/openssh-aix After installing the prerequisites using the following commands,
1. rpm -i zlib-1.1.4-3.aix4.3.ppc.rpm
2. rpm -i prngd-0.9.23-3.aix4.3.ppc.rpm AIX 5.2 uses /dev/urandom
3. rpm -i openssl-0.9.7d-1.aix5.1.ppc.rpm
4. rpm -i openssl-devel-0.9.7d-1.aix5.1.ppc.rpm
How to Check OfficeScan License
1. Go to http://www.trendmicro.com/ website
You will see Update Center tab on the right hand.
 to be continue
to be continue
Wednesday, May 13, 2009
Window 2K3 error Netlogon 5774
 Windows 2003 domain controllers may log one or more of the following events in the System event log: Netlogon 5774 - Registration of the DNS record record_name_and_dns_info failed.
Windows 2003 domain controllers may log one or more of the following events in the System event log: Netlogon 5774 - Registration of the DNS record record_name_and_dns_info failed.-----------------------
Netlogon 5774
The Netlogon 5774 error message is logged in the System event log when the Netlogon service on a domain controller cannot register an individual resource record. The event description contains the name of this resource record and other DNS parameters that are used for the registration attempt, for example:
Event Type: errorEvent
Source: NETLOGONEvent
Category: NoneEvent
ID: 5774
Date: x/x/xxxx
Time: xx:xx:xx
PMUser: USER
Computer: COMPUTER
to be Continue